Mechanical radiator for FORD,Radiators for FORD,performance fit FORD vehicles JIANGSU KALLER AUTO PARTS THCHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.jskaller.com
Although great progress has been made in the development of smart home technologies, there is still a long way to go in order to truly realize the “people-oriented†service nature of smart homes. The future of smart homes should be focused on the "intelligence" of serving homeowners, that is, based on changes in the family environment, owner's location, owner's sentiment, time, and other factors, and actively provide adaptive services. For this reason, it is necessary to continue to focus on the development of key technologies for smart homes. This paper studies a smart home system that supports semantic reasoning, and introduces semantic elements in the smart home IoT system to realize semantic reasoning of smart homes and achieve the purpose of real smart home services. .
1 things semantic architecture <br> <br> to solve the problem of heterogeneous interconnected and intelligent platform for the rapid development of networking technology arising in the course, many scholars and organizations of Things semantic technology has been extensively studied. In the development of Internet of Things standards, the International Organization for Standardization OneM2M introduced semantic technologies into the Internet of Things to enable it to support knowledge inference and enhance the intelligence of the Internet of Things. Combining with the demand for semantic object networking in the smart home environment, this paper improves the oneM2M semantic function model and proposes the semantic structure shown in FIG. Major improvements are reflected in the following two aspects: Adding content related to device control functions, including instruction sets and instruction processing modules; setting device object pools, storage device objects, including device instances corresponding to physical devices, and abstracting out the basic functions of physical devices Abstract devices, mash-up generated virtual devices. 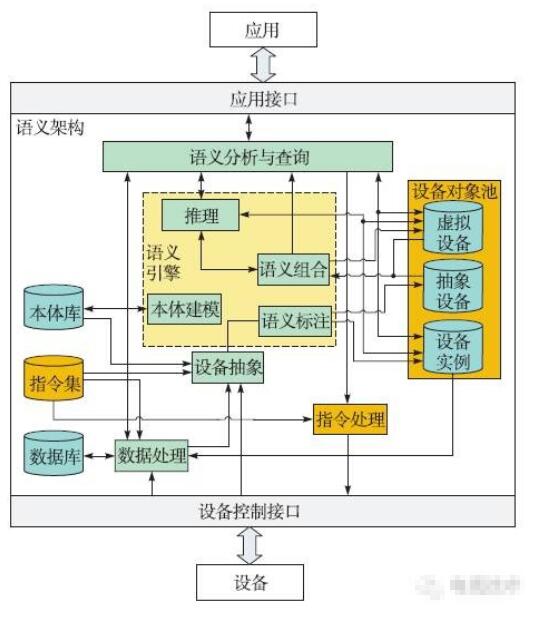
Semantic analysis and query: semantic analysis (including direct parsing, or inferring inference process) of application-side instructions, and conversion into REST instructions for CRUD operations on resource URLs, and sending them to data processing or instruction processing modules.
Reasoning: For the instructions sent by the semantic analysis and query module, based on the preset rules, acquire the object resources in the existing devices (including device instances and virtual devices) and determine the instruction types; when the unique object resources are not acquired, the semantics are invoked. Combination module.
Semantic combination: According to specific rules, it provides new services to users by aggregating abstract devices and virtual devices from different sources. This process can be triggered by user requirements and can also be actively triggered by the platform.
Ontology modeling: off-line process, for each new resource (including equipment, users, etc.), pre-created ontology model.
Semantic annotation: Add semantic information to device instances and abstract devices.
Device abstraction: When a new physical device goes online, it creates a device instance corresponding to one, and abstracts the main functions of the physical device, resulting in several abstract devices.
Instruction processing: Convert platform internal instructions into private instructions that are identifiable by the physical device and complete the encapsulation of the instructions.
Data processing: On the one hand, the correctness and validity of the data sent from the physical device are verified and converted into a unified format and stored in the database. On the other hand, the database is established and maintained, and the data in the database is modified or deleted as needed. And other operations.
Ontology library: used to store ontology models.
Device object pool: consists of three parts. The device instance corresponds to the physical device. The abstract device abstracts the basic functions of the physical device. The virtual device is generated through a mash-up process.
Instruction library: used to store the private instruction set (such as machine code) that can be identified by the physical device, and maintain the mapping relationship between the internal instructions of the platform and the private instructions of the device.
Database: Used to store processed device data.
2. Construction and query of smart home body 2.1 Construction of smart home ontology The demands of the quality of life in modern homes are increasing day by day. Smart home systems need to meet the needs of home owners for various life services. In most articles, there are only single requirements for home monitoring and lighting. Conduct the analysis. To this end, starting from comprehensiveness, this article analyzes the needs of various services such as family safety, health, comfort, communication, wealth management, education, and entertainment. Due to space limitations, only the structural diagram is given, as shown in Figure 2. 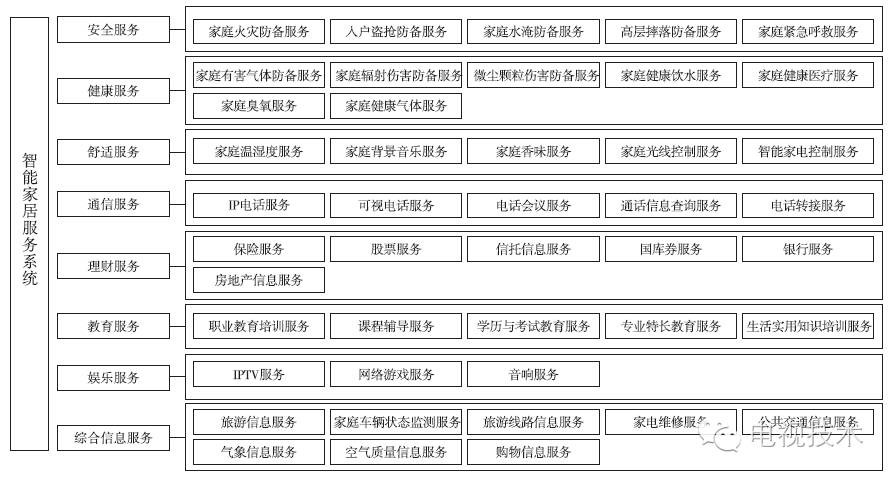
As can be seen from the figure, providing a large number of humanized services for homes in a complex smart home environment requires the support of nearly 100 smart devices such as home appliances, equipment, equipment, and sensors. In the above-mentioned Internet of Things semantic architecture, the construction of device ontology in the smart home environment is the basis of semantic reasoning. For each specific model of smart home device, it is necessary to establish an ontology model corresponding to it. In this paper, the design is shown in Figure 3. The ontology model structure shown includes five parts: basic equipment information DeviceInfo, equipment running status, running status, function Function, rule Rule, and data data. 
Among them, DeviceInfo home device basic information includes device id number, device name, ontology model resource identifier, device model, device manufacturer, device type and other information; RunningStatus device operating status is used to describe the operation mode of the device, various functions on/ Off status and other information; Function device function records the corresponding device private instructions, parameter list, whether to support automatic mash-up and other information; Rule device rules record the operation of the device or data processing rules; Data device data records the data type, The current value, data unit and data processing rules and other information.
This article adopts the OWL language recommended by W3C to carry out ontology modeling for home devices. OWL mainly includes two elements: class Class and property Property. The relationship between class and class can be expressed by means of triples. Objects can be represented by using Object Property. Relationships between classes, use Data Property to represent the relationship between object class and data class. Using the Protégé software to build a smart home device body OWL description file, due to space reasons only intercept part, as shown below: 
2.2 Smart home semantic query After the home device ontology model is designed, the description of the instance model resource can be based on the semantic information of the device resource and the annotation is based on the semantic ontology. In addition, the search target object in many semantic data, using SPARQL language query, the basic format is as follows:
In the query, the parameter data in the .owl file is matched according to the triple relationship described by SPARQL to find the target object.
3 Smart Home service semantic reasoning <br> <br> ontological model-based semantic technology with increasing complexity of the business relationship has been growing, the Semantic Web rules language (SWRL) to the Semantic Web Ontology Language (OWL) as the basis, It fuses the RuleML multi-rule description method and has strong rule description ability and semantic reasoning ability. This paper adopts SWRL technology to carry out semantic expression and rules establishment for many complex services in smart home, and combines reasoning with JENA reasoning machine.
In the smart home environment to provide users with personalized services, you can define a variety of different service modes. Based on the rules of the definition of various home furnishing equipment functions, a new SWRL rule is defined for semantic combination to provide users with humanized services. The SWRL rule consists of the antecedent premise part, the consequent conclusion part, and a number of element atoms, and is specified using the Uniform Resource Locator URI, which is expressed as follows:
Among them, the element can be a data type function C(x) and a relational type function P(x,y),sameAs(x,y), differentFrom(x,y) or builtIn(r,x), where "? "Indicates the x variable.
Take the protection of domestic harmful gas carbon monoxide, volatile organic compound (VOC) gas (such as formaldehyde), second-hand smoke, household fumes, and harmful gases around the home as an example, and provide various gas detection sensors, fresh air, doors, windows, and alarms. Some rule definitions as shown in Table 1 are shown. 
4 System Implementation The system platform uses the Apache embedded Web server. The development language and environment use Java and Eclipse. The database uses the lightweight Sqlite database. Ontology modeling uses Protégé ontology editing tools and uses OWL language to formally describe. Finally, Jena inference engine is used to test the inclusion and consistency of ontology models and the inference of custom rules. The system operation interface is shown in Figure 4. 
5 Summary <br> <br> With the popularity of "people-oriented" concept, people-based Internet of Things smart home system no longer satisfied with simple remote control and management functions, and pay more attention to its automatic and intelligent. Based on analyzing a variety of smart home services, this paper constructs smart home ontology knowledge, and studies and implements a smart home system with semantic reasoning function. This work has guiding significance for the intelligent application development of smart home systems.
In recent years, with the development of information technologies such as Internet of Things, mobile Internet, and artificial intelligence, smart home systems such as security, entertainment, energy saving, and health with various functions have begun to integrate into millions of households, and the widespread use of advanced technologies has made ordinary people's daily lives The quality has improved significantly. Complex smart home systems often have a variety of smart devices with different functions. The Internet of Things awareness module acquires sensory data from home devices and then converts these functions into user-oriented terminal remote control through the functions provided by the home smart integration platform. Monitoring and other services.
Figure 1 Improved IoT Semantic Architecture
Figure 2 smart home service structure
Figure 3 smart home device body model structure
Table 1 Definition of Domestic Harmful Gas Prevention Service Rules
Figure 4 smart home service management platform operation interface (screenshot)