Ammonia nitrogen (NH3N) is present in water as free ammonia (NH3) or ammonium salt (NH4+), the composition of which depends on the temperature and pH of the water. For the determination of NH3N in industrial wastewater, the laboratory generally uses ammonia in the wastewater to separate, absorb, and volume the total amount of the ammonia in the wastewater, and then titrate or colorimetrically determine the accuracy and reproducibility of the first method. Although it is good, the operation is time-consuming; the second method has the characteristics of rapid and convenient, but the accuracy of the measurement of the wastewater containing NH3N is somewhat poor, and both methods are troublesome and time consuming. The NC2 quick nitrogen analyzer is a nitrogen determination device developed by the author that integrates heating, pumping, absorption, and titration. It does not condense with water, and can continuously measure the sample without replacing the vessel. The entire measurement process is approximately 20 minutes. High precision of measurement. The application of this rapid nitrogen determination instrument for the determination of industrial waste water containing higher NH3N, especially for the synthesis of ammonia and other fertilizers, has the advantages of rapidness, accuracy and reagent saving. The minimum detection limit is 0.1 mg/L, which can fully meet the industrial wastewater requirements. NH3N monitoring accuracy requirements. The analysis method is described below.
1 Principle of the method The sample is distilled under the action of concentrated alkali, ammonia nitrogen is released, absorbed with excess boric acid, titrated with hydrochloric acid standard solution by means of mixed indicator. The main reaction:
Distillation: (NH4)2SO4+2NaOH 2NH3↑+2H2O+Na2SO4
Absorption: 4H3BO3+NH3NH4HB4O7+5H2O
Titration: NH4HB4O7+HCl+5H2O NH4Cl+4H3BO3
2 instruments and reagents NC2 type rapid determination of nitrogen device (see Figure 1) by the reaction part, absorption titration part. Hydrochloric acid standard solution: 0.025 mol/L; Mixing indicator: Weigh 0.5 g bromocresol green and 0.1 g methyl red in 100 ml ethanol, and use sodium hydroxide solution (about 0.1 mol/L) and hydrochloric acid solution ( About 0.1 mol/L) was adjusted to purple-red (pH about 4.5); Neutral boric acid solution: mass concentration was 20 g/L, mixed indicator was added, and purple red was adjusted with the above sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid solution.
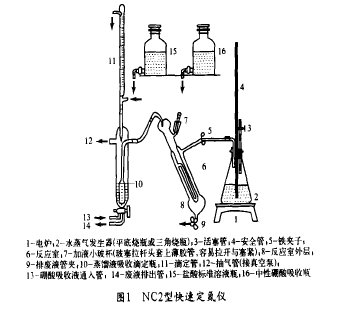
3 Analysis steps
(1) Take a sample of 100 ml in a 250 ml beaker, add 1+1 sulfuric acid dropwise until it is acidic (purified by a fixed nitrogen indicator) and excess 1 ml, heat and evaporate to about 10 ml on an electric furnace. Cool and leave it as the test solution (If the wastewater contains more than 2.0 mg/L of NH3N, then take 10 ml directly as the test solution).
(2) The water vapor generation bottle 2 is filled with 2/3 volume of acidic water (add a few drops of mixed indicator and adjusted to red with sulphuric acid) and boiled in an electric furnace, and then the fireproof plate is covered on the electric furnace to keep the water temperature around 90°C. . Open the clamp 5, close the piston 3, and in the case of evacuation, add the hydrochloric acid standard solution to the dropper 11 and align the zero position. About 50 ml of neutral boric acid absorbing solution is added to the absorption bottle 10 . The test liquid (depending on the NH3N, can directly take the waste water sample) flows into the reaction chamber 6 from the small glass cup 7, and the glass cup is rinsed with a small amount of water. Put a rod-shaped glass stopper, and pour 10 ml of 400 g/L sodium hydroxide into a small glass cup, pull the glass stopper to let the sodium hydroxide solution slowly flow into the reaction chamber, and quickly install the glass stopper when the flow is finished. Place water in the glass cup and always check for leaks (after adding sodium hydroxide solution, there should be excessive alkali in the reaction solution, otherwise it needs to be added). Absorption of ammonia in the absorption bottle by the boric acid absorption solution causes the indicator to turn blue-green, and the temperature rises. It must be continuously titrated with a hydrochloric acid standard solution at all times to maintain the neutrality of the solution (the indicator maintains the original magenta color) until the absorption solution maintains purple. Red does not change to the end point, note the volume of hydrochloric acid standard solution consumed. Open the piston 3, close the clamp 5, open the clamp 9, pull open the glass plug on the small glass cup, draw out the waste liquid from the reaction chamber, and flush the reaction chamber with water 3 to 4 times to remove the rinse water. Close the clamp 9, open the clamp 5, open the piston 14, and use the waste liquid extraction tube to extract the waste liquid from the absorption titration bottle. At the same time do a blank test.
4 Analysis results
m (NH3N) = (AB) × N × 14 × 1 000V mg / L formula 14 - nitrogen molar mass, g / mol;
N - hydrochloric acid standard solution concentration, mol/L;
A - the amount of hydrochloric acid standard solution consumed, ml;
B - blank consumption of hydrochloric acid standard solution, ml;
V - water sample volume, ml.
5 Results and Discussion
5. 1 Selection of heating temperature This device uses steam to heat the reaction chamber under the condition of pumping, and ammonia is volatilized under alkaline conditions. Experiments show that steam generator temperature can be 90 °C. Boiling is too severe, the temperature is too high when ammonia is sucked, ammonia volatilizes too quickly, too late to titrate, so that the result is too low; the steam temperature is too low, the reaction rate is too slow, it will also affect the measurement speed and reduce work efficiency.
5.2 Control of pumping speed Since the device eliminates the water cooling device, it is necessary to control the proper pumping speed, and continuously titrate the ammonia in the absorbing solution to maintain the neutrality of the absorbing solution, so as to achieve the best absorption effect. . Too small suction will affect the absorption and titration, and it is better to continuously generate bubbles in the absorber.
5. 3 Pre-dosing of titration solution To increase the effect of ammonia absorption, a predetermined volume of hydrochloric acid standard solution can be added in advance according to the ammonia content of the sample. When parallel experiments are performed, hydrochloric acid standard solution consumed by about 90% may be added in advance according to the volume of hydrochloric acid standard solution consumed for the first time to facilitate absorption.
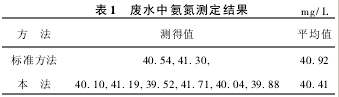
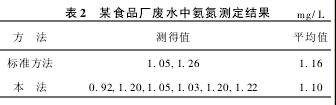
5. 4 Comparison of the results of the determination of waste water samples
(1) Collect a sample of synthetic ammonia plant wastewater, take a sample of water 10 ml, and directly add it to the reaction chamber, and measure it in parallel for 6 times according to the above steps, and measure it twice in accordance with the national standard method (titration method). The result is shown in Table 1. In this method, 20.00 mg/L ammonia nitrogen was added, the measured value was 59.58 mg/L, and the recovery rate was 95.3%.
(2) Collect the waste water from a food factory and take a sample of 100 ml. Concentrate it to about 10 ml according to the above procedure and measure it in parallel for 6 times. Measure it twice with Nessler's reagent colorimetric method. The results are shown in Table 2. This method was used to spike 2.00 mg/L ammonia, the measured value was 3.24 mg/L, and the recovery rate was 104%.
It can be seen from the above results that the results of the determination of wastewater with different ammonia nitrogen content by this method are all within the tolerance allowed by national standards. Because this method is continuously carried out, ammonia is immediately titrated with a hydrochloric acid standard solution when it is released, without the use of a standard curve or a spectrophotometer, which greatly increases the analysis speed, and is particularly worthy of promotion in the analysis of industrial production fertilizers.
Learn more about top instrument products such as agricultural machinery area meter and rice mill.
Hydraulic Release Bearing,Hydraulic Clutch Release Bearing,Auto Hydraulic Release Bearing,Auto Hydraulic Clutch Release Bearing
ZHEJIANG BENTENG INTELLIGENT BRAKE SYSTEM CO.,LTD , https://www.cnnakol.com